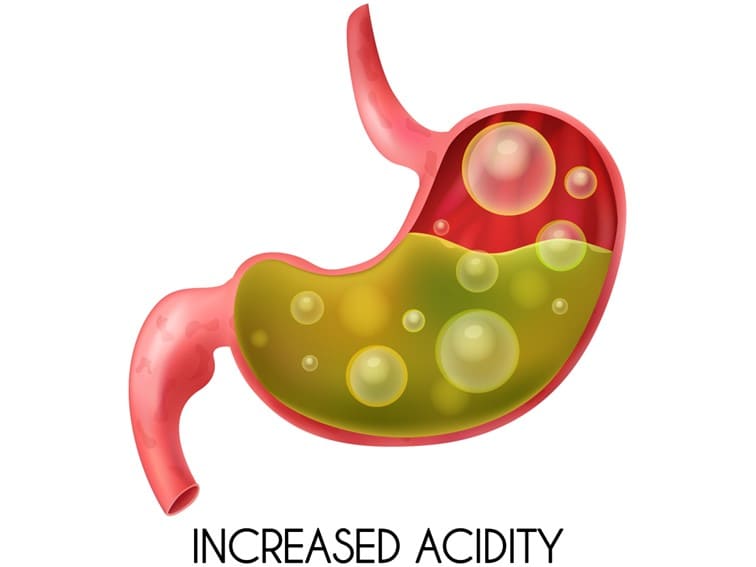
Acidity problems: The gastric glands of your stomach produce and secrete acid – which is necessary to digest the food. When excess acid is produced than needed for the digestion process, the condition is known as acidity. In some cases, normal stomach acid flows back to the esophagus. This condition is known as acid reflux (GERD). The most common symptom of this condition is a burning sensation and chest pain in the breastbone.
What are the common causes of acidity?
Acidity causes: In a majority of cases, lifestyle-related factors are responsible for acidity and stomach problems. They include the following:
- Excessive eating (overeating)
- Unhealthy eating habits
- Excessive consumption of tea or coffee
- Eating at irregular times or skipping meals
- Eating just before sleeping
- High intake of table salt
- Consuming a sugary diet or a diet low in dietary fiber
- Consumption of spicy food
- Excessive consumption of fat-rich foods such as fried foods, doughnuts, pizza, extremely oily, fatty, and spicy foods
- Excessive intake of carbonated drinks, caffeinated beverages, and soft drinks
Use of medications
Regular use of pain-relieving medications, over-the-counter medications, other temporary medications as well as prescription medicines can cause acidity problems. For instance, medications such as antibiotics, medicines for controlling high blood pressure, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; anxiety and depression medications can cause acidity.
What other disorders can cause acidity problems?
Irritable bowel syndrome, peptic ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and other conditions can also lead to acidity.
What are the other causes of acidity?
- Eating gas-forming vegetables such as cabbage or cauliflower
- Excessive consumption of non-vegetarian food
- Lack of physical exercise
- Frequent consumption of alcohol
- Smoking
- Excessive stress
- Insomnia (Lack of sleep)
- Mental health issues
Do you know – people who have dental health issues, connective tissue disorders, diabetes and asthma, and breathing problems – such as sleep apnea are more prone to acidity? In women, those who are approaching menopause, obese women, depressed women, and even pregnant women suffer from acidity.
What are the symptoms of Acidity and Acid Reflux Disease?
Acidity Symptoms are not the same in all people. Bloating blenching, and gas formation indigestion is the most common symptoms of acidity. However, symptoms differ from person to person. For instance, chest pain and burning sensation below the breast bone are the most common symptoms of acid reflux. The other symptoms of acidity that are uncommon may include:
- Indigestion
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Restlessness
- Heaviness in the stomach after taking meals
- Post-meal discomfort and sometimes pain
- Burning sensation and pain in the stomach
- Bad breath
- Burning sensation and pain in the chest
- Frequent hiccups or burping for no apparent reason
- Difficulty in swallowing food
- A feeling of food being stuck in the throat
- Burning sensation and pain in the throat
- Bitter-taste or prolonged sour taste in the mouth due to acid reflux (regurgitation)
Bottom Line
Acidity problems once in a while are alright as you can set it right with some slight lifestyle modification – eating and sleeping habits. But when you frequently suffer from acidity and indigestion or any other acidity-related symptoms, there should be a cause for concern. If a person frequently suffers from bouts of acidity – what does it mean – say – he or she has symptoms lasting for two or more days per week – on a regular basis. It means that there might be an underlying cause associated with acidity. It is therefore advisable that they should consult a specialist doctor without wasting any time.