Gallbladder specialist in Hyderabad – Dr. Datta Ram U
Gallbladder removal surgery, also known as cholecystectomy, is a standard surgical procedure that involves the removal of the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ located under the liver that plays an important role in the digestive process by storing and releasing bile. However, in some cases, the gallbladder can develop problems, leading to a range of symptoms that can affect your quality of life. In this article, we will explore the reasons why you might consider gallbladder removal surgery, the types of surgery available, and the recovery process.
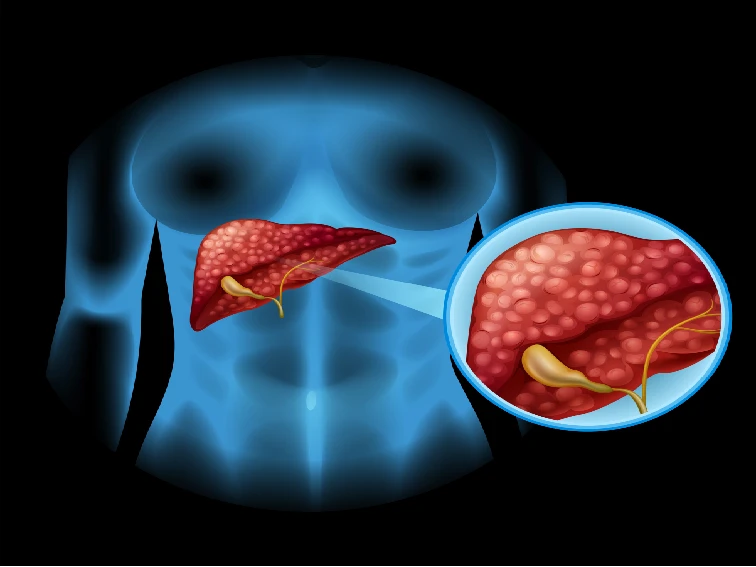
What is the Gallbladder, and what does it do?
Before we dive into the reasons why you might need gallbladder removal surgery, it is essential to understand what the gallbladder is and what it does. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ that sits under the liver on the right side of the abdomen. Its main function is to store and release bile, a fluid produced by the liver that helps digest fat. When you eat, the gallbladder contracts and releases bile into the small intestine, where it breaks down the fat in the food you have eaten.
When is Gallbladder Removal Surgery Necessary?
A gallbladder specialist doctor in Hyderabad recommends surgery if a person has one or more of the following conditions:
Gallstones
Gallstones are small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder and can cause pain and other symptoms. Gallstones can develop when there is too much cholesterol or bilirubin in the bile, or when the gallbladder does not empty properly. If you have gallstones that are causing pain or other symptoms, your doctor may recommend gallbladder removal surgery.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is a condition in which the gallbladder becomes inflamed. This can happen when a gallstone gets stuck in the opening of the gallbladder, causing a blockage. Cholecystitis can cause severe pain, fever, and other symptoms. If you have cholecystitis, a gallbladder specialist in Hyderabad may recommend gallbladder removal surgery to prevent future attacks.
Biliary Dyskinesia
Biliary dyskinesia is a condition in which the gallbladder does not empty properly, causing pain and other symptoms. Biliary dyskinesia can be caused by a variety of factors, including nerve damage and certain medications. If you have biliary dyskinesia that is causing pain or other symptoms, your gallbladder specialist in Hyderabad may recommend gallbladder removal surgery.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition in which the pancreas becomes inflamed. In some cases, gallstones can cause pancreatitis by blocking the pancreatic duct, which is the tube that carries digestive enzymes from the pancreas to the small intestine. If you have pancreatitis caused by gallstones, gallbladder specialist in Hyderabad may recommend gallbladder removal surgery to prevent future attacks.
Types of Surgery to remove gallbladder
There are two main types of gallbladder removal surgery: laparoscopic cholecystectomy and open cholecystectomy.
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the most common type of gallbladder removal surgery. It involves making several small incisions in the abdomen and inserting a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera and surgical instruments attached. The surgeon uses the laparoscope to see inside the abdomen and remove the gallbladder through one of the small incisions.
Open Cholecystectomy
Open cholecystectomy is a more invasive type of gallbladder removal surgery that is usually only performed if laparoscopic cholecystectomy is not possible. It involves making a larger incision. The surgeon directly accesses the gallbladder through this incision to remove it.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery
Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery, also known as laparoscopic cholecystectomy, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the gallbladder. This type of surgery offers several benefits compared to traditional open surgery, including:
1. Smaller Incisions
During laparoscopic gallbladder surgery, the surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen rather than one large incision. This minimizes scarring and reduces the risk of infection.
2. Faster Recovery Time
Because laparoscopic gallbladder surgery is minimally invasive, it typically results in a faster recovery time compared to open surgery. Most patients are able to go home the same day or the day after the surgery and can return to work and normal activities within a week.
3. Less Pain and Discomfort
Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery is less painful than open surgery because it causes less trauma to the surrounding tissues. This means that patients experience less pain and discomfort after the surgery and require less pain medication.
4. Lower Risk of Complications
Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery is associated with a lower risk of complications compared to open surgery. This includes a lower risk of bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding organs.
5. Higher Success Rates
Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery has a high success rate, with most patients experiencing complete relief of their symptoms after the surgery. In addition, the recurrence rate of gallstones after laparoscopic cholecystectomy is low.
6. Improved Quality of Life
Patients who undergo laparoscopic gallbladder surgery often experience an improvement in their quality of life. This is because the surgery relieves the symptoms of gallbladder disease, such as abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, laparoscopic gallbladder surgery offers several benefits over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, faster recovery time, less pain and discomfort, lower risk of complications, higher success rates, and improved quality of life. If you are considering gallbladder surgery, talk to the best gallbladder specialist in Hyderabad about whether laparoscopic gallbladder surgery is right for you – don’t delay in seeking the appointment of Dr. Datta Ram U.