Crohn’s disease symptoms | Complications | Dr. Datta Ram U
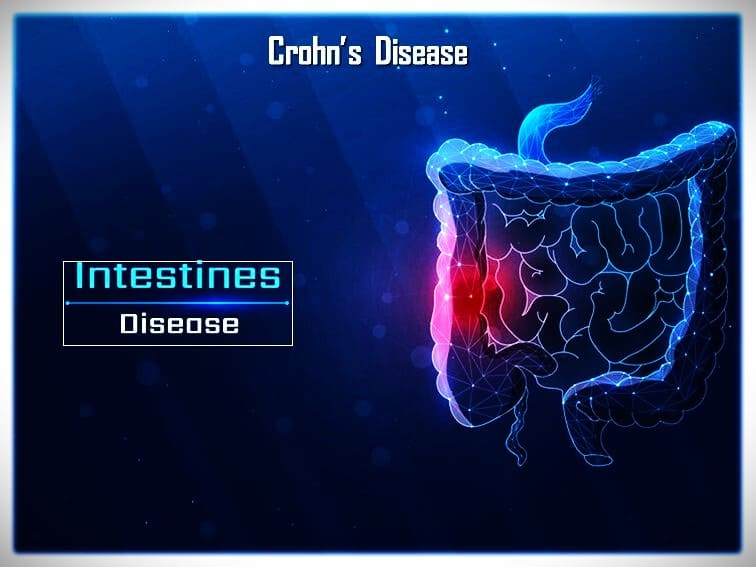
Crohn’s disease causes inflammation (swelling in the tissues of the digestive tract). It is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Crohn’s disease can be debilitating and painful. It affects different areas of the digestive tract in different people. Any part of the large intestine or small intestine is involved. In some people, the disease is only in the colon. The inflammation most commonly affects the small intestine. It can also spread to the deeper layers of the bowel.
Crohn’s disease symptoms
The signs and symptoms can be mild, moderate to severe. Symptoms manifest gradually, but, in some cases, symptoms come on suddenly. There may be periods of no signs and symptoms in between (remission). The typical signs and symptoms include:
- Abdominal cramps
- Malnutrition
- Abdominal pain
- Severe diarrhea
- Fever
- Reduced appetite
- Mouth sores
- Blood in stool
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
Unusual Signs and Symptoms
In some cases, Crohn’s disease symptoms are reported outside the intestinal tract. Some people with severe Crohn’s disease may experience iron deficiency anemia, kidney stones, inflammation of the bile duct or liver; inflammation of skin, eyes, and joints. In children delayed growth and sexual development is seen.
Crohn’s Disease Causes
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown, but stress, anxiety, and diet can aggravate the condition. Many experts believe that there are several factors that play a role in the development of Crohn’s disease – for instance: the immune system and heredity.
The risk factors for Crohn’s disease may include age, family history, lifestyle, ethnicity, and other habits such as smoking and the use of NSAIDs.
Complications of Crohn’s Disease
Malnutrition: When you have persistent cramping, diarrhea and abdominal pain, you will not eat properly and your intestine doesn’t absorb enough nutrients. Therefore, you may develop anemia, low iron, and vitamin B12 deficiency.
Anal Fissures: If you have constipation and painful bowel movements – a small tear occurs in the tissue that lines the anus. It may lead to infection and painful bowel movements.
Fistulas: These are abnormal connections that can develop near or around the anus (perianal).
Ulcers: Open sores or ulcers can develop anywhere in the digestive tract – mouth, intestine or anus, or in the genital area (perineum).
Other problems: Gallbladder or liver disease, arthritis, osteoporosis, and anemia (low iron) are some of the other health conditions associated with Crohn’s disease.
Skin disorders: Hidradenitis suppurativa is a condition seen in some people with Crohn’s disease. It is a skin disorder with deep nodules and abscesses in the armpits, groin, and under the breasts or in the genital or perianal region.
Blood Clots: The risk of the formation of blood clots increases in the arteries if a person has Crohn’s disease.
Diagnosis of Crohn’s disease
The diagnosis of Crohn’s disease is made only after ruling out the other possible causes for the signs and symptoms. Your gastroenterologist may recommend several tests to rule out the cause of other health conditions and diagnose Crohn’s disease.
Blood tests include test to check for anemia and infections, and to check liver function. A stool test may be recommended to look for hidden (occult) blood, infections, or parasites.
Colonoscopy: To have a complete view of the entire colon, your doctor uses a thin, flexible, lighted tube with a camera at the end is used. Your doctor also takes tissue sample (biopsy) for laboratory analysis. Spotting of granulomas (clusters of inflammatory cells) indicates Crohn’s disease.
Crohn’s Disease Treatment
Treatment helps in reducing signs and symptoms. It can provide relief from persistent inflammation and bring long-term remission. However, there is no permanent cure for Crohn’s disease. Furthermore, no single treatment works for everyone. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation that prompts the signs and symptoms and to improve long-term prognosis by restricting complications.
Medical treatment involves anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, antidiarrheal drugs, pain relievers, vitamins, and minerals supplements. If drug therapy, diet, lifestyle changes, or other treatments don’t relieve your signs and symptoms, your doctor may recommend surgery.
When should you see a doctor?
If you notice any changes in your bowel habits with any of the typical signs and symptoms of Crohn’s disease such as diarrhea lasting more than two weeks, nausea and vomiting, blood in your stool, abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, and also fever – then see your doctor.