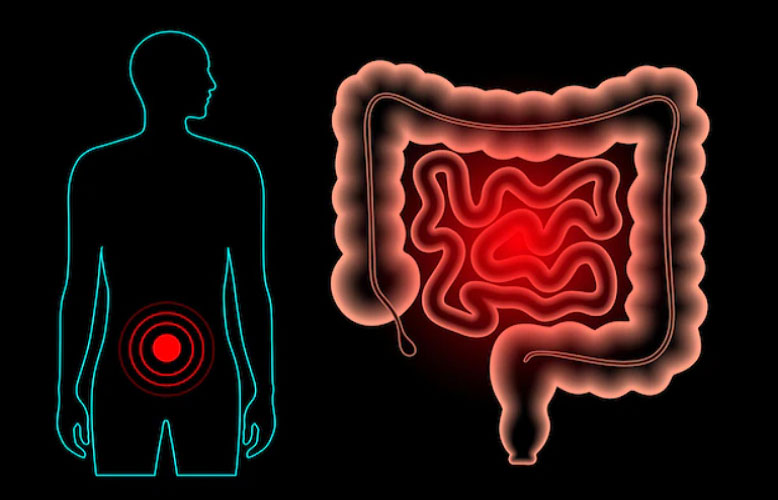
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a common condition of the digestive system mostly affects the large intestine. It interferes with the normal functions of the large intestine (colon). Though it does not cause any severe health problems, it can give you trouble for long. If you have this problem, your life may change. Taking part in daily activities, travel and going to social events can become troublesome for those who suffer from IBS. Which means, you may not be able to work properly, miss work, or may need to change your work setting. The symptoms of this disorder generally begin after 20 years – and may continue for long. IBS is common in women compared to men. Some people think that it may cause Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and colon cancer, but IBS does not cause any of these conditions. Let us understand how this common abdominal problem can trouble you and what measures you should take to manage it comfortably.
What are the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)?
People with IBS experience different types of symptoms including abdominal discomfort, pain, change in bowel habits or infrequent bowel movements: either go too often or less often and have thin, liquid, soft or hard stool. Some individuals may have constipation, bloating, crampy or severe abdominal pain or diarrhea. Some people pass mucus with stool and have irregular bowel movements. Many people feel better after a bowel movement. In some cases, stress can make the symptoms of IBS worst.
What are the Causes of IBS?
What causes IBS is still unknown, but there are some factors that could play a role including the following: stronger and weaker contractions of the muscles of intestine – longer and stronger contractions can cause diarrhea, bloating and gas and weaker contractions can make the food passage slow and lead to dry and hard stools. Another factor could be bacterial overgrowth and after a severe infection caused by bacteria or virus (gastroenteritis). In some people immunological response may cause inflammation in the intestine due to increased number of immune cells – which may cause pain and diarrhea. Poor coordination of signals between the nerves of the digestive system and brain can prompt changes in the normal digestive process and result in constipation, pain and diarrhea. According to some research studies, the colon becomes sensitive to some meals, medicines, food, emotions and stress in individuals who have IBS.
What is the function of Colon?
Colon absorbs nutrients, water and salt. Muscles, nerves and hormones control the movement of the colon. The motility of the colon helps in passing the contents through it. The contents of the colon move towards the rectum and strong contraction causes bowel movement. Relaxation and contraction of sphincters muscles and pelvic muscles in a coordinated manner helps in smooth bowel movement.
How Is IBS Diagnosed?
When you experience the symptoms of IBS, it is better to see your gastroenterologist. He will examine you and ask about your previous medical history and the symptoms you are experiencing. Diagnosis is based on physical examination, symptoms and medical history. However, your doctor may order a few other tests such as stool examination, blood tests and colonoscopy to rule out other health conditions.
Is IBS Linked to Other Diseases?
IBS is also known as spastic colon, mucus colitis or spastic bowel. IBS does neither cause any colon tissue damage nor colon cancer. And therefore, people with IBS are not at a risk of developing colon cancer. There is no connection between IBS and ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease.
What Is the Treatment for IBS?
The treatment for IBS is aimed at relieving symptoms as there is no specific cure for it. Gastroenterologists prescribe medicine to treat the symptoms and advice their patients to take medicines as instructed and also suggest changes in the diet and lifestyle of the patients. Most of the doctors advice patients to manage their diet and stress. Doctors also prescribe medicines for relieving abdominal pain, reducing constipation, bloating, diarrhea and muscle spasms. Some physicians recommend antispasmoic drugs or antidepressants to reduce diarrhea. Laxative or fiber supplements may also be prescribed. Some people tend to manage the symptoms of IBS with OTC medicines and laxatives, but they should consult their doctors. The treatment for IBS may differ from person to person as there is no specific medicine or a combination of medicines that work for everyone. Your physician will examine you, ask you about your symptoms, counsel you and support you in managing your symptoms.
Can IBS be Managed with Diet?
You can manage the symptoms of IBS with some lifestyle changes – especially the changes in your diet, eating habits and by managing stress. The best thin that you can do is making notes of all that you do routinely – especially the food you eat. By doing so you can observe which food is making the symptoms worst. If you notice some wheat products, milk and other dairy products are causing your symptoms then replace those products with better foods. You can prefer fiber rich cereals, whole breads, vegetables and fruits to reduce the symptoms of constipation. Avoid coffee, colas, and carbonated beverages. Eating smaller meals or smaller portions more often can help you relieve IBS symptoms.
Bottom Line
The signs and symptoms of IBS are severe only in a small number of people. Mild symptoms can be managed with diet, stress management and making other lifestyle changes. Symptoms that are more frequent and distressing can be managed by medication, diet and counselling.
Remember! Persistent severe abdominal pain, pressure, bleeding, fever, and weight loss are the symptoms indicative of other serious conditions like cancer. Therefore, if you notice any new symptoms including bleeding or blood in stools and weight loss, then never ignore such symptoms as people with IBS may have other health conditions. In such cases, physicians order further investigations to rule out life-threatening conditions like colon cancer as a part of diagnosis of exclusion.