Pancreatitis treatment in Hyderabad | Dr. Datta Ram U
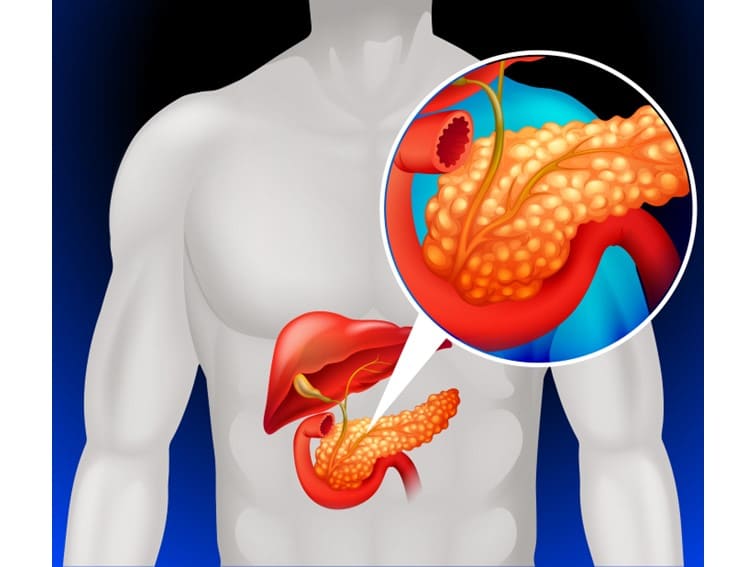
The pancreas is a small organ (long and flat) of the human digestive system with a very crucial role in digestion. It lies behind the stomach in the upper abdomen. The pancreas produces digestive enzymes and hormones for metabolism. Hormones produced by the pancreas play an important role in regulating and processing glucose in the body.
Pancreatitis Types
Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis. There are two types of pancreatitis: acute and chronic pancreatitis. When pancreatitis develops suddenly and quickly and lasts only for a few days, it is an acute type. In some cases, pancreatitis develops progressively over a few months or years. This is known as chronic pancreatitis. A less severe and mild type of pancreatitis improves with proper treatment and management. Chronic and severe pancreatitis can cause serious and life-threatening complications.
Symptoms
The most prominent symptom of acute pancreatitis is abdominal pain. In some cases, the condition settles down within a few days or weeks. However, it may become very serious and severe.
Signs and symptoms associated with acute pancreatitis include the following:
- Pain in the upper abdomen
- The pain radiates to the back
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Rapid pulse
- Fever
- Tenderness when touching the abdomen
Chronic pancreatitis symptoms include the following:
- Abdominal pain
- Pain becomes worse after eating
- Pain mostly felt in the upper abdomen
- Oily, smelly stools (steatorrhea)
- Losing weight without trying
What are the causes of acute pancreatitis?
The most prominent cause of acute pancreatitis is excessive alcohol consumption and the formation of gallstones. The other causes may include:
- hypertriglyceridemia: High levels of triglyceride in the blood
- Certain medications
- Hypercalcemia: High levels of calcium in the blood may be due to hyperparathyroidism [overactive parathyroid gland]
- Abdominal surgery
- Pancreatic cancer
- Injury to the abdomen
- Infection
- Cystic fibrosis
- Trauma
- Obesity
In some cases, the cause is unknown (idiopathic pancreatitis)
Bottom Line
Acute pancreatitis can become a chronic inflammatory condition inducing devastating damage which may turn deadly. The mortality rate associated with all types of pancreatitis remains at above 10 to 12% despite huge medical advancements over the past few decades. The main reason for this could be the slow progress of the condition and relative inaccessibility of the organ as there are no easy ways to see the pancreas directly. The available tests, diagnostic methods, techniques and approaches, and imaging techniques are inadequate.
Pancreatitis treatment in Hyderabad
Difficulties in the diagnosis often delay treatment leading to complications. Apart from the acute and chronic types of pancreatitis, other forms such as hereditary may progress slowly over several years causing significant damage to the person. Those who suffer silently are subjected to enduring pain and malnutrition and could become prone to pancreatic cancer in the long run.
Early detection and diagnosis of the condition are important for the best pancreatitis treatment in Hyderabad at Sunshine Hospitals. If you have any of the above signs and symptoms of acute or chronic pancreatitis, meet Dr. Dattaram U.